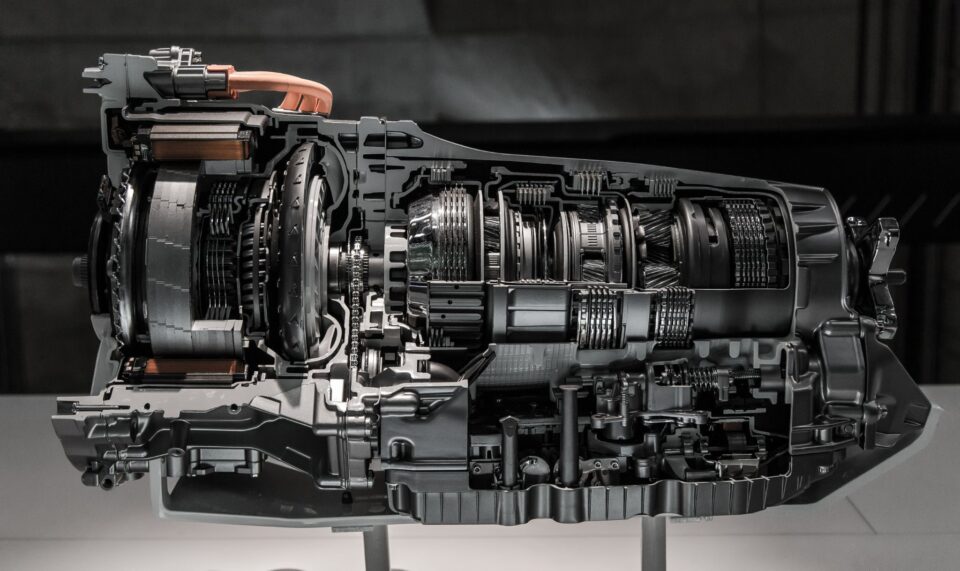
The gearbox is the most common component of a transmission system. The gearbox with gears and gear trains is called a 5-speed transmission. Torque and speed conversions from a spinning power source are accomplished with the help of such devices. Find more information about Dorman 200 transmission
The transmission system of a car is crucial because it transfers power from the combustion engine to the tires. As it is unsuitable for slowing down or halting, it helps the engine operate at a high relative speed.
Explain what a transmission system is.
The TRANSMISSION SYSTEM is the part of a car that transfers power from the engine to the wheels. The clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, differential, and final drive shafts are all parts of the drivetrain; It serves in a wide variety of non-vehicular contexts when speed and torque conversions from a rotating power source are required.
Applications:
Transmission systems are crucial not just for automobiles but also for certain stationary applications like wind turbines. Transmissions are not only found in automobiles, but also in farming, manufacturing, mining, and other machinery.
Functions:
- The engine must be able to be connected and disconnected from the remainder of the powertrain in a smooth and shock-free manner.
- Change the ratio of engine torque to wheel torque.
- The methods to effect a reversal of power flow are made available.
- Allow for electricity to be transmitted at varying distances and angles.
- Allow a decrease in speed of 5:1 between the engine and the driving wheels.
- It is also possible to switch the direction of the current at right angles.
- Make sure there’s a way to change the speed at which the wheels are driven as needed.
- be able to withstand the force of a torque response, a driving push, and a braking effort.
The Transmission System Components
- Propeller shaft
- clutch
- gearbox
- Interchangeable joints
- Tires
- real axles
Types of transmission system:
- Transmission with a Manual Shift (MT)
- Transmission with Automatic Shifting (AT)
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
- Automated Manual Transmission (AM)
Manual Transmission:
All gear changes in a manual gearbox system are made by the driver using a shifter and clutch pedal. It’s common to refer to this gearbox type as a “stick shift” or “standard” gearbox.
Automatic Transmission:
Transmissions with automated modes use a planetary gearset, a torque converter, and clutches or bands. Automatic transmissions are used to change through forward gears in a vehicle. Aside from driving forward, neutral, or backward, drivers have minimal manual control.
Automated Manual Transmission:
The automated manual gearbox is mechanically identical to the conventional manual transmission in every respect. However, the clutch is not used by the driver with an automatic manual gearbox, hence the clutch pedal is unnecessary. The clutch is operated by an electrical, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuator. The acronym “DSG” stands for “Direct Shift Gearbox” and describes this transmission technology.
Continuously Variable Transmission:
The continuously variable transmission utilizes pulleys, belts, and sensors to achieve a customizable driving ratio. To maintain a continuous speed curve with no interruptions for gear shifts, gear wheels are removed. They improve efficiency and gas economy by keeping the engine running at its optimal power setting.